
양방향 막대 그래프 그리기 2 - 천단위 콤마, 레이블 위치

위에 링크에서 지난시간 양방향 그래프를 그리는 기본적인 방법부터 알아보았었다
이번 시간에는 이 그래프를 좀 더 깔끔하게 표현할 수 있는 방법을 알아보겠다.
1. 천단위 콤마 표시하기
가독성을 좋게 하기 위해 보통 천단위에 콤마를 표시하는데, 파이썬에 여러 방법이 있다.
예를 들어, 10대 남자의 인구 수를 표시한다고 하면 아래의 두 방법을 쓸 수 있다.
1) f-string
Male_teens = Population.iloc[1, 0]
print(f"{Male_teens:,}")
2) format 함수
print(format(Male_teens, ',d'))
이번에는 f-string을 이용한 방법을 사용해서 레이블을 천단위 콤마 표시를 해본다면, 아래의 그림처럼 결과가 나온다.
(비교를 위해 남성에만 콤마 표시를 해봤다. 역시 좀 더 가독성이 좋게 표현된다.)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(15,6))
ax.barh(Population.index, -Population['Male'], color = 'lightgrey')
ax.barh(Population.index, Population['Female'], color = 'lightsteelblue')
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{Population['Male'][i]:,}", # 천단위 콤마
xy = (-Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'center', ha='right')
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{Population['Female'][i]}",
xy = (Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'center', ha='left')
ax.legend(['Male', 'Female'], loc="lower right")

2. 천단위 절사
위에처럼 콤마로도 충분하지만 숫자가 커서 그래프 밖으로 튀어나온다. X축을 조정할 수 있지만 이번에는 천단위 아래를 절사해보는 방식을 사용해보겠다.
엑셀의 "#,##0," 형식처럼 파이썬에도 천단위 절사가 가능한 함수가 있을 거 같은데 찾지를 못해 약간의 야매로 1000을 나누어서 그 몫만 표시하는 방법을 써보겠다.
인구 수에 1000을 나누고 반드시 정수형으로 바꿔주는 int 함수를 쓰던지 나누기를 몫만 반환하는 "//" 이걸 써줘야 한다.
그렇지 않으면, 소수점도 같이 나온다.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(15,6))
ax.barh(Population.index, -Population['Male'], color = 'lightgrey')
ax.barh(Population.index, Population['Female'], color = 'lightsteelblue')
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{int(Population['Male'][i]/1000):,}", #천단위 절사
xy = (-Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'center', ha='right')
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{Population['Female'][i]}",
xy = (Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'center', ha='left')
ax.legend(['Male', 'Female'], loc="lower right")

아래는 처음 그래프와 여성 데이터에도 천단위 콤마와 천단위 절사 모두 적용시킨 그래프이다.


3. 레이블 위치 조정
레이블을 상하 위치 또는 좌우로 조정할 수 있는 va, ha 함수가 있다.
va는 상하로 조정하는 'top', 'bottom', 'baseline', center_baseline' 4가지 옵션이 있고,
ha는 좌우로 조정하는 'center', 'right', 'left' 이렇게 3가지 옵션이 있다.
이 옵션들은 직접 실습을 해보면서 각 상황마다 가장 적절한 위치를 찾는 게 더 나을 것 같다.
다만, 이 옵션들이 우리가 기본적으로 생각하는 방향과 반대로(?) 적용되는 거 같다.
예를 들어, 남성의 va는 'top'으로 여성은 'center'로 설정을 했는데 아래 그래프처럼 오히려 남성이 더 아래쪽에 위치한 결과를 보여준다. 또한 좌우도 이유를 모르겠지만 서로 반대로 인식된다.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(15,6))
ax.barh(Population.index, -Population['Male'], color = 'lightgrey')
ax.barh(Population.index, Population['Female'], color = 'lightsteelblue')
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{int(Population['Male'][i]/1000):,}",
xy = (-Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'top', ha='right') # 레이블 위치
for i in Population.index:
ax.annotate(f"{Population['Female'][i]//1000:,}",
xy = (Population['Male'][i], i),
va = 'center', ha='left') # 레이블 위치
ax.legend(['Male', 'Female'], loc="lower right")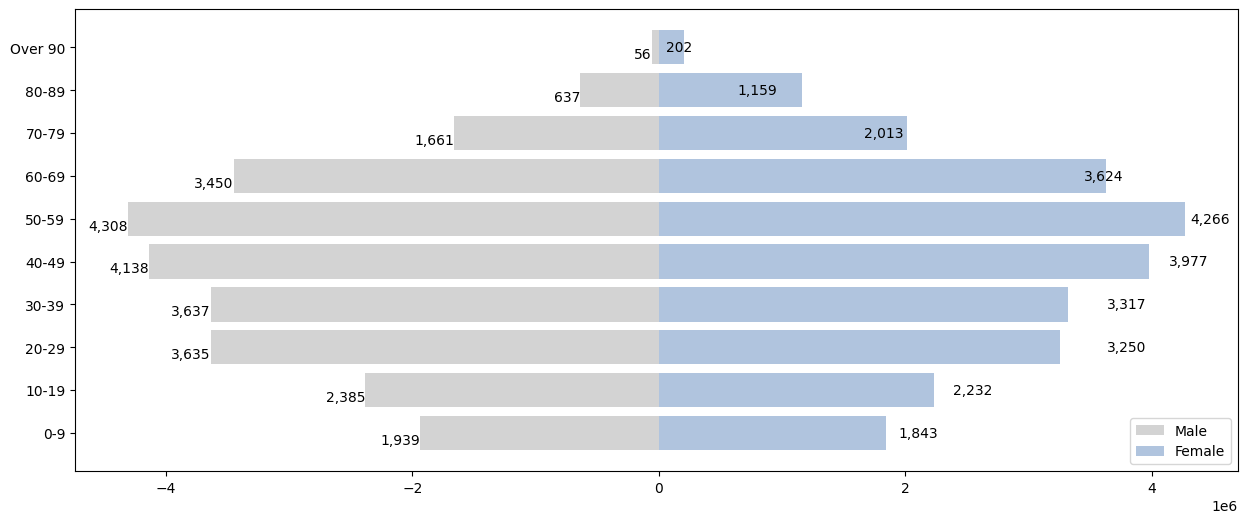
'self.python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python] 양방향 막대 그래프 그리기 - barh 함수 사용 (0) | 2023.05.20 |
|---|---|
| [python] seaborn으로 HeatMap 그리기 - 2 (최대값/최소값, Cbar, tick, Label 조절하여 그래프 그리기) (1) | 2022.12.05 |
| [python] seaborn으로 HeatMap 그리기 - 1 (0) | 2022.11.06 |
| [python] 데이터 프레임 전처리 - replace 이용하기 (0) | 2022.07.03 |
| [python] 숫자 데이터 자리수 맞추어 표시하기(앞에 0 채워주기) - zfill() (0) | 2022.06.27 |



